
Purdue University in the U.S has recently published an research on Nature claiming that they have developed a new technology called confined-pulse laser deposition that can produce synthetic nano diamond on the graphite's surface.
Purdue University in the U.S has recently published an research on Nature claiming that they have developed a new technology called confined-pulse laser deposition that can produce synthetic nano diamond on the graphite's surface and special graphic patterns. The technology has an important influence on the future nana diamond biosensors, quantum computers, fuel cells, and the next generation computer chips.
Gary Cheng, the associate professor in the Department of Industrial Engineering in Purdue University says that compared with traditional synthetic diamond process technology, the new technology is able to deposit nano diamond without high pressure and high temperature. The whole experiment was done in room temperature, and there was no need for high temperature and high pressure vessels, which has decreased the costs. In addition, the experiment also developed a new writing technology that could selectively write nano diamond in designed patterns on the workpiece surface.
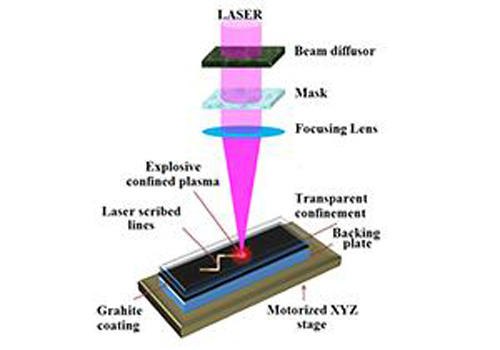
Cheng notes that the resulting nano diamond coating is very strong and could be used for high-temperature sensors.
The researchers made the discovery while studying how to strengthen metals using a thin layer of graphite and a nanosecond-pulsing laser. A doctoral student noticed that the laser was either causing the graphite to disappear or turn semitransparent.
"The black coating of graphite was gone, but where did it go?" Cheng says. It has been proved in the following research that the graphite had turned into diamond. The research team confirmed that the structures are diamond using a variety of techniques including transmission electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, and the measurement of electrical resistance.
Author: Liwei Chu
Copyright: iAbrasive.com--Abrasives & Diamond Tools Market