
SiC, short for Silicon Carbide, which has for many years attracted attention due to its superior characteristics and performance over silicon, is being increasingly researched and adopted in a variety of applications in many areas.
SiC, short for Silicon Carbide, which has for many years attracted attention due to its superior characteristics and performance over silicon, is being increasingly researched and adopted in a variety of applications in the industrial, automotive, railway, consumer, and other sectors in order to improve energy savings and efficiency.
Formula E, one of the world’s first all-electronic motor racing series held by FIA, presented a prime opportunity for showcasing the performance advantages of SiC in EVs. With Season 3 just underway on October 9 in Hong Kong, the challenge was to find the most efficient method of transferring energy provided by the battery to the road. To accomplish this, ROHM partnered with Formula E team Venturi to incorporate SiC Schottky Barrier Diodes (SBDs) in the drive inverter to enhance the performance of the powertrain system by significantly improving thermal efficiency and switching speeds. Season 4 will see the integration of SiC MOSFETs, which should result in further efficiency gains.
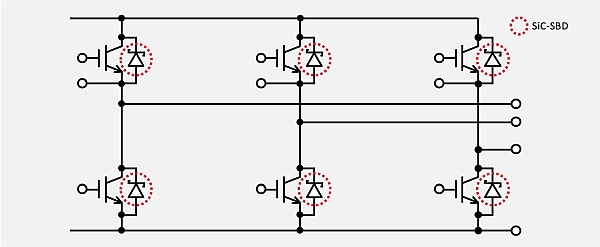
SiC SBDs (for use in Formula E drive inverters)
SiC SBDs deliver lower switching loss and forward voltage characteristics, reducing conduction losses for greater efficiency and performance. As a result they are often utilized in high-efficiency power source devices.
SiC SBDs featuring breakdown voltages from 600V and up are readily available. Compared to silicon FRDs (Fast Recovery Diodes), SiC SBDs provide much lower reverse recovery current and recovery time, which translates to significantly reduced recovery loss and noise emissions. Furthermore, unlike silicon FRDs, these characteristics do not change significantly over current or operating temperature, allowing system designers to improve efficiency, lower the size of heat sinks, and increase switching frequency to reduce the size and cost of magnetics.
SiC SBDs are increasingly applied to circuits such as PFC (Power Factor Correction) and the secondary side of bridge rectifiers in switch mode power supplies. Today’s applications range from air conditioners, solar power inverters, and EV chargers to industrial equipment and more.
ROHM’s current SiC SBD lineup includes devices from 600V to 1700V, with current ratings from 5A to 40A.
Key advantages of SiC SBDs in Formula E inverters
Lighter weight - SiC SBDs reduce inverter weight by 2kg
Improved efficiency - Electric efficiency is increased by 1.7% while the volume of heat dissipation components reduced by 30%.